Explain the Different Feeding Styles of Benthic Dwellers Including
Benthic zone which describes the layers closer to the bottom of the water body and pelagic zone which includes the free water column that interacts with the surface layers of a water body. Difficulties of describing extent to which marine environment is inhabited include immense size of marine habitat and inaccessibility.
Discuss the adaptations many aquatic insects have that allow them to live in the different habitats.

. On land there are many different habitats or ecological niches for species to inhabit. They include dragonfly and stonefly larvae snails worms and beetles. A 70-day experiment was conducted to examine the carbon isotopic signatures of A.
Rocky bottoms are home to many types of animals including. The benthic invertebrates typically include sea stars sea anemones corals worms sea urchins sponges bivalves crabs and many more. Benthic bottom-dwellers insects can cling sprawl climb and burrow.
Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the. The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean lake or stream including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The benthic zone includes submerged plants and animals like crabs prawns fishes and lobsters that will remain on the bottom of the marine layer.
Currently 250000 documented marine species which rep. This weeks highlighted opisthobranch is one of these exceptions. In addition to being sensitive to changes in the streams overall ecological integrity benthic macroinvertebrates have other advantages as.
They suck sediment and small benthic crustaceans called amphipods from the. While midwater trawling catches pelagic fish like mackerel bottom trawling catches groundfish species and invertebrates like cod rockfish and shrimp. Only 14 of all known species on Earth.
Theorist Neil Fleming coined VARK as a model for learning. In order to increase the. Contrast the proposed feeding style of Pentacrinites allowed it to return to the benthic realm but in an inverted attitude.
Only 14 of species live in ocean. However this model can be further expanded into the following 7 different learning styles. More habitats or niches means more species may be present.
Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates such as crustaceans and polychaetes. In the ocean the benthic environment has many habitats or. Their food tons of krill other zooplankton crustaceans and small fish are licked off their baleen using their tongue and swallowed.
B gradients near- to. Caprella penantis feeds primarily by filter-feeding and scraping. Plankton and nekton can float drift and swim.
Others like the three-ridge mussel can be more than ten inches long. The basic construction of Isocrinida including species surviving on present deep-sea bottoms is a rigid body capsule calyx with a fixed number of sutured plates and a flexible tegmen plus three kinds of flexible appendages1 The arms support rows of pinnules and tube feet for passive filter feeding in a current coming from the aboral side. Clams mussels and crayfish.
Three species ofcaprellid amphipods were described with very different feeding types. Suspension feeding organisms such as sponges and barnacles grazers such as urchins chitons limpets and abalone and carnivores such as crabs octopus and fishes. They lack a backbone are visible without the aid of a microscope and are found in and around water bodies during some period of their lives.
Apart from their basic geospatial location difference many other factors help us to differentiate between these. The 7 Learning Styles. And Luconacia incerta depends almost entirely on predatory habits Caine 1974.
Many benthic creatures particularly clams and worms serve as food for larger economically important species such as blue crabs striped bass spot croaker and white perch. What are the species distribution on earth. One may explain benthic and pelagic life-styles with the statement that most opisthobranchs are benthic bottom dwellers and most fish are pelagic ie they live up in the water column.
Matched tissuesediment samples were collected from A background areas over a range of depths throughout the Strait of Georgia southern Gulf islands Juan de Fuca Strait and west coast Vancouver Island. Japonicus feeding on 6 different types of diets with the ingredient of either pure powder of. We investigated the effects of two tube-dwelling organisms amphipods Corophium insidiosum and chironomid larvae Chironomus.
Any water body will have two distinct zones. Up to 10 cash back Burrowing benthic animals belonging to the same functional group may produce species-specific effects on microbially mediated nitrogen N processes depending upon different ecological traits. Each species may uniquely adapt itself for a particular environment.
Many bottom-feeding fish eg flatfish gobies and mullets feed on harpacticoid copepods and optionally ostracods but usually not throughout their entire life because their diet changes with age and they shift their food preferences as they grow and meiofauna becomes too small to meet their nutritional requirements Grossman 1980. Paracaprella tenuis feeds as a filter-feeder scraper scavenger and predator. Metabolic variability in unsighted pelagic groups figure 3 b appears to reflect different feeding strategies ranging from float-and-wait predators to the more active tactile foraging found in some gymnosome molluscs.
Unre-lated pseudoplanktonic crinoids of earlier times show. Benthic meaning bottom-dwelling macroinvertebrates are small aquatic animals and the aquatic larval stages of insects. Visual auditory readingwriting preference and kinesthetic.
Benthic taxa tend towards slightly more robust bodies and higher metabolic rates relative to gelatinous zooplankton. Benthic foraminiferal food sources were examined in the central part of Sagami Bay Japan water depth 1450 m based on an in situ feeding experiment with 13C. Lastly neuston surface dwellers can skate or jump along the surface.
Gray whales a family of baleen whales are bottom feeders. Additionally the bacteria decomposers and detritus-feeders that live at the bottom of the Bay break down waste products and dead plants and animals. Some benthic macroinvertebrates like midges are small and may grow no larger than one-half inch in length.
Visual learners prefer to see things drawn out or in graphs to understand concepts. During this complex history most adaptational changes required only heterochronic shifts in the devel-opment of tegmen arms pinnules stem and cirri. A description of all tissue types including feeding method typical taxa and habitat usage is given in Table 1.
Benthic trawling involves towing a net at the very bottom of the ocean while demersal trawling is the process of towing the net just above the benthic zone.
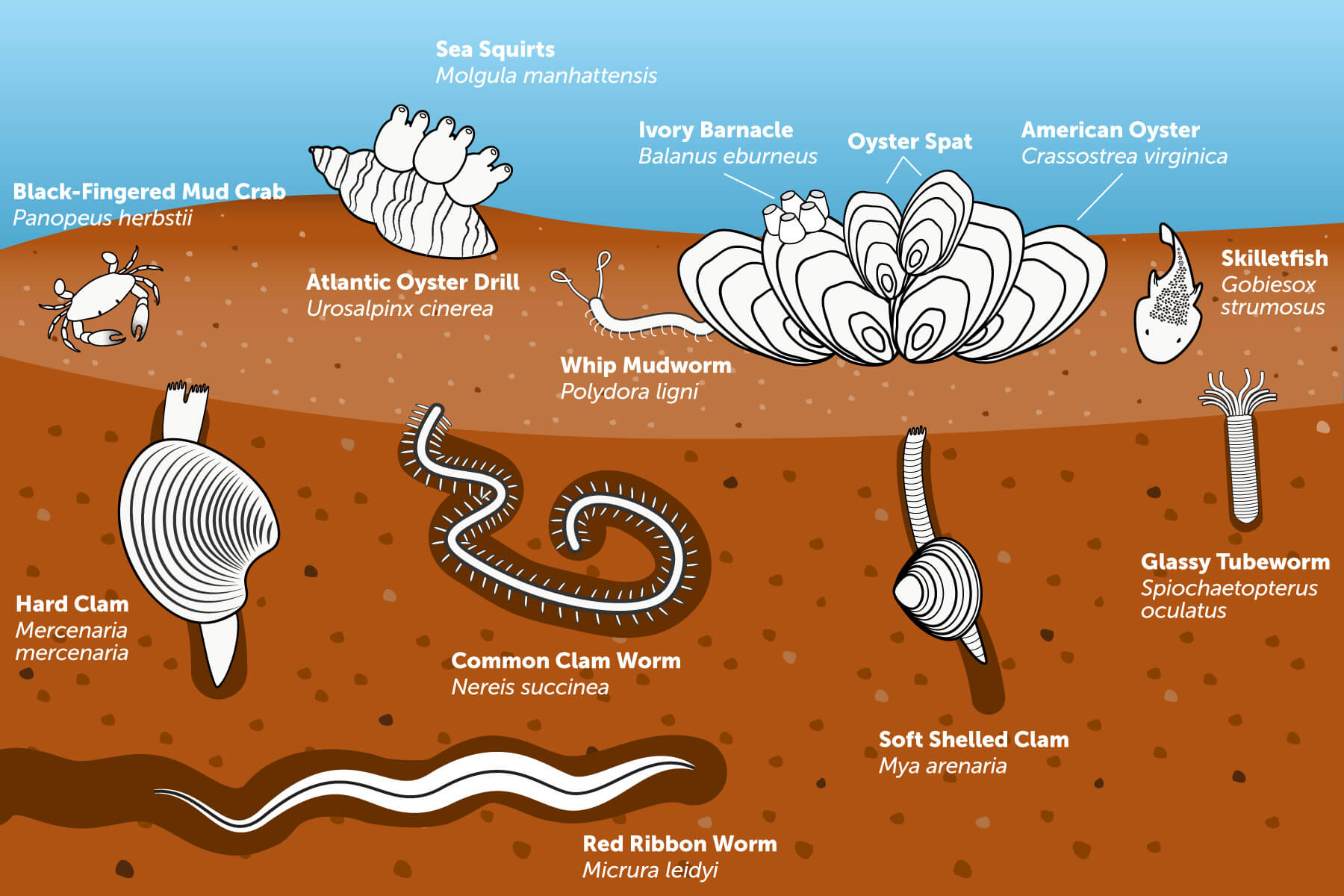
Life At The Bottom Chesapeake Bay Program

Macrobenthos An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Oceanography Final Exam Flashcards Quizlet

Plankton And The Benthos From The Top To The Bottom

Plankton And The Benthos From The Top To The Bottom

Schematic Drawing Of Different Feeding Behaviours Of European Download Scientific Diagram

What Are Benthic Animals Worldatlas

Macrobenthos An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Three Types Of Animal Microbe Interactions That Interfere With Benthic Download Scientific Diagram

Plankton And The Benthos From The Top To The Bottom

Pdf Linking The Bottom To The Top In Aquatic Ecosystems Mechanisms And Stressors Of Benthic Pelagic Coupling

Benthic Pelagic Coupling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Functional Diversity In Marine Ecosystems Marinespecies Introduced Traits Wiki
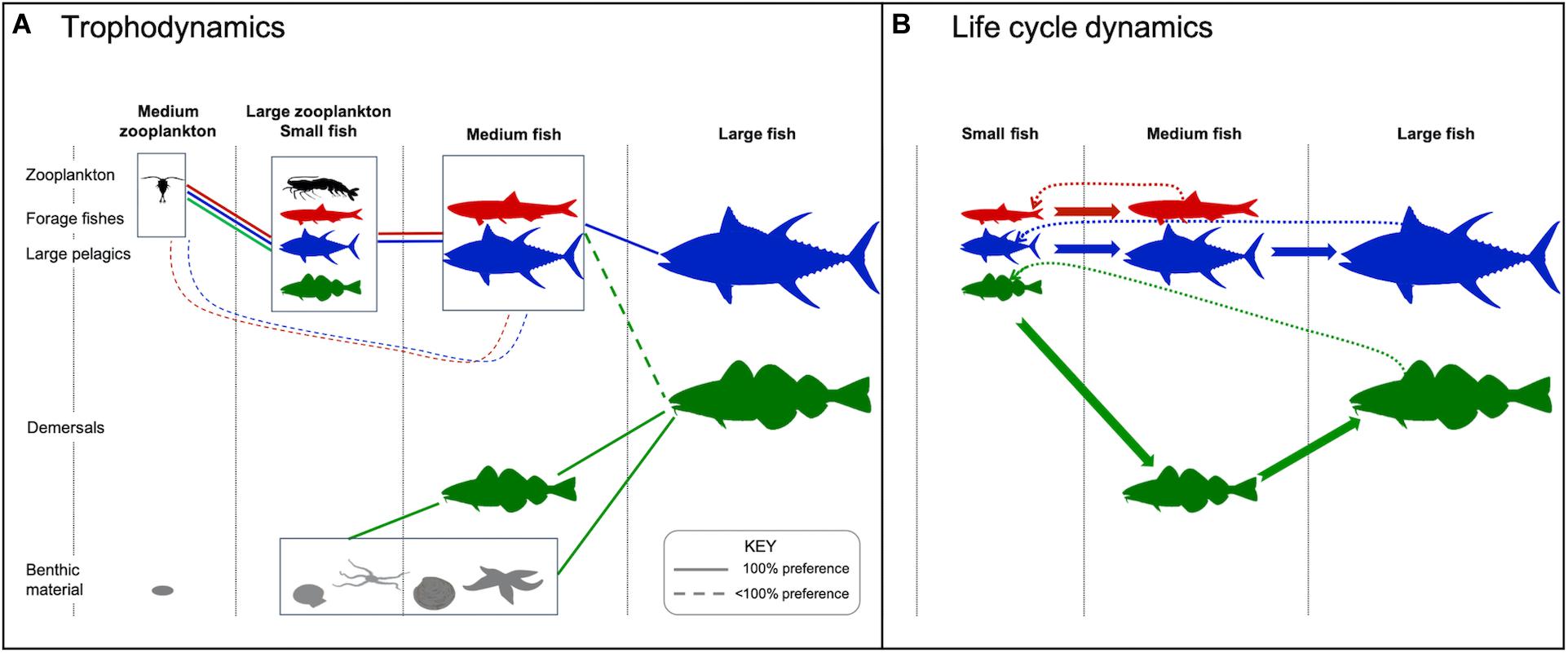
Frontiers Large Pelagic Fish Are Most Sensitive To Climate Change Despite Pelagification Of Ocean Food Webs Marine Science

Macrobenthos An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Plankton And The Benthos From The Top To The Bottom
Figure C 3 Feeding Types Of Benthic Organisms After Rhoads 1974 Download Scientific Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment